The final analysis consisted on the FEM structure analysis with critical forces applied, to test the resistance of the designed structure.
An essential part of the bogie original design has been the constant check of the structure. Tests were performed on the CATIA Structural Analysis module.
The most critical parts are the bogie base structure, which supports all the other parts, the guide itself, and the locking cog part, which is responsible for the support of the booms when still.
First of all we performed a static analysis to understand what forces are applied on the different parts.
Static analysis
Forces applied on the bogie are essentially on 2 axis: the weight of the booms on the vertical direction and the force of the wind on horizontal direction. The first is balanced by the locking cogs while the bogie is still and by the cable when moving, the latter by the four wheels which impede the movement of the bogie away from the guide.
Bogie base structure
The base structure has to balance the force of the wind that tends to move the bogie outside of the guide.
Our data show a total force in the worst wind condition (40 knots) of 30kN for a 73 square meter sail. Being our sail about 4 times bigger, we assumed a total maximum force of the wind of 120kN.
The FEM analysis shows a maximum stress of 130 Mpa in an unrealistic worst condition (all the force of the wind is supported by the still bogie), that is anyway abundantly less than the yield strength of steel.
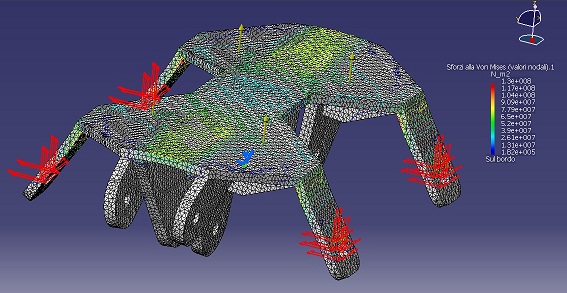
Locking cogs structure
From our data, the weight of the single boom is 11 tons, and from our model results that its center of mass is positioned at about the 41% of its lenght. Therefore, assuming a total lenght of 28 meters, at about 11.5 meters from the bogie we analized and about 3.3 meters from the other bogies on the moving part. This means that the total force experimented by the bogie is about 40% of the weight of the 2 booms, so 90kN. This force's direction is upwards, although being the bogie symmetrical, direction of the force is essentially unimportant.
This force is active when sails are opened, so while the bogie is still and the locking cogs are down. This means that the cogs have to sustain this force. The central spring keeps the cogs down on the gauge line, impeding the rotation of the cogs. The FEM analysis in worst condition is the following
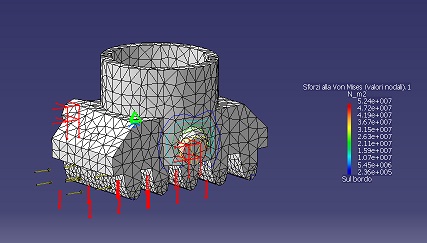
showing a maximum stress, on the two supports, smaller than the maximum acceptable. To make the structure more solid it is also possible to enlarge the supports.
Bogie structure
FEM analysis on the other parts of the bogie structure show stresses abundantly below the maximum yield, making the parts analized above the most critical parts.