Stress analysis: Blocking cam
The stress analysis have been done in 6 cases: maximum load carried out by the pin or by the spring and a middle point between motion start and maximum load, both in opening and closing pahses.
The cam has been constrained with soft springs, method allowing to analyze in a better way then ground fixing stresses and strains distribution on rotating component. In order to use this method the insertion of reaction forces has been required.
The mesh setting is:
- Element dimension: 0.05, in relation to the average component dimension
- Local setting: 0.05 mm, on the fillet between shaft and cam body
- Local setting: 0.05 mm, on the spring support surface
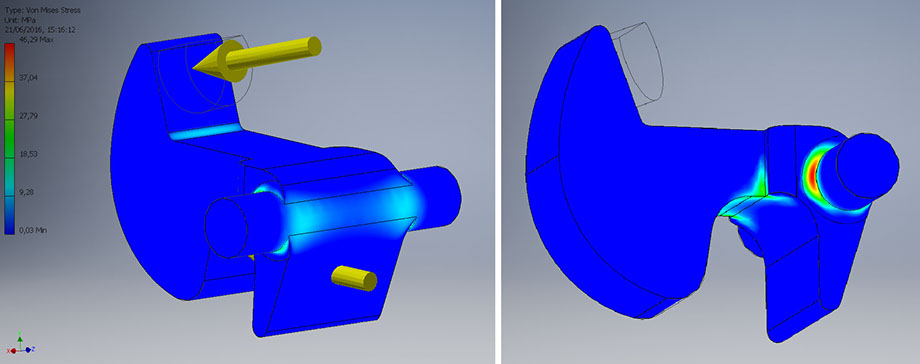
Opening: middle point between start and maximum load
Contact force: 57.7 N
Elastic force: 28.87 N
Maximum Von Mises stress: 46.29 Mpa
Maximum strain: 0.03 mm
Minimum safety factor: 2.38
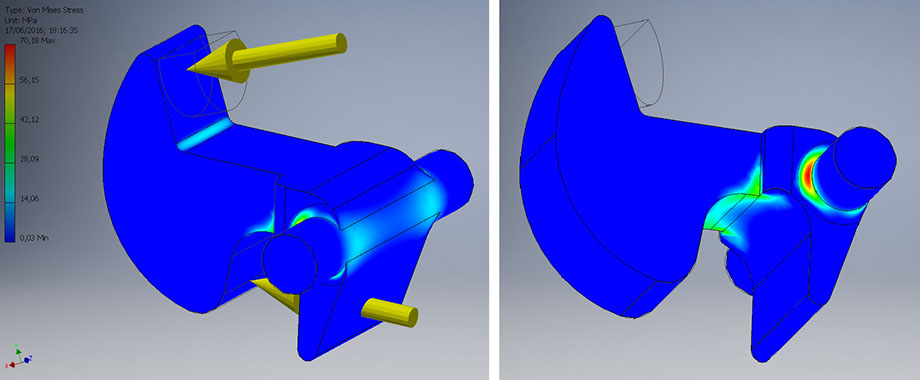
Opening: maximum load carried out by the pin
Contact force: 78 N
Elastic force: 47.03 N
Maximum Von Mises stress: 70.1 Mpa
Maximum strain: 0.04 mm
Minimum safety factor: 1.57
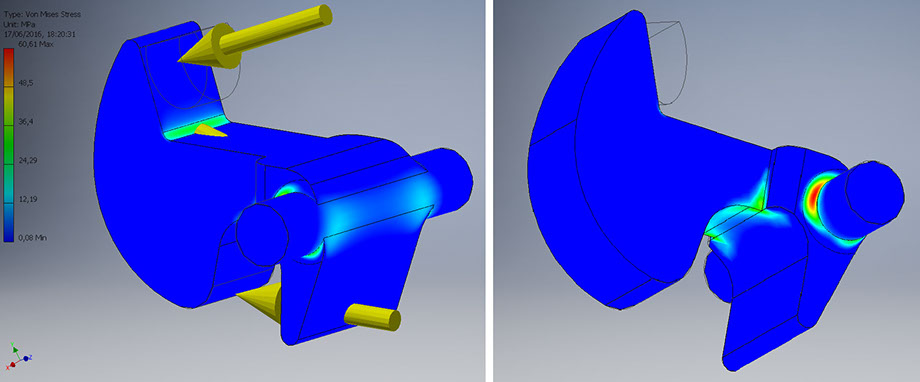
Opening: maximum load carried out by the spring
Contact force: 65.99 N
Elastic force: 60.72 N
Maximum Von Mises stress: 60.61 Mpa
Maximum strain: 0.04 mm
Minimum safety factor: 1.81
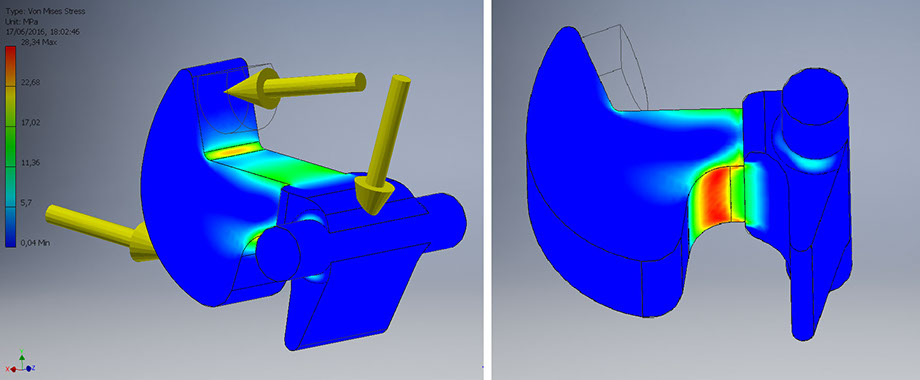
Closing: middle point between start and maximum load
Contact force: 46.09 N
Elastic force: 21.43 N
Maximum Von Mises stress: 28.34 Mpa
Maximum strain: 0.03 mm
Minimum safety factor: 3.88
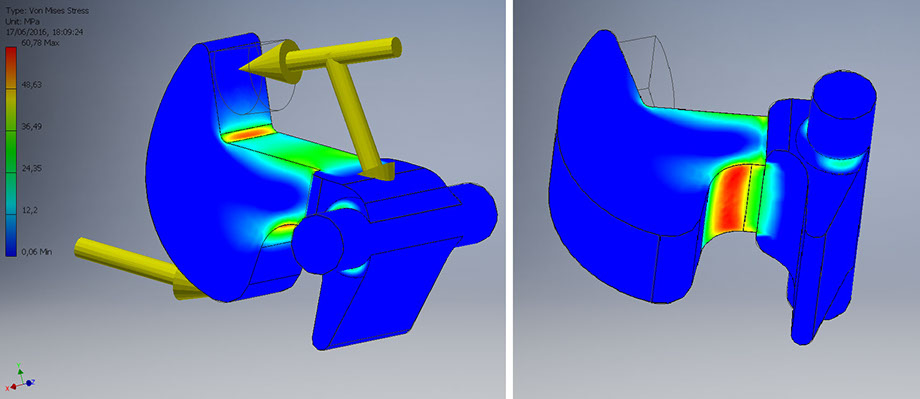
Closing: maximum load carried out by the pin
Contact force: 72.5 N
Elastic force: 54.09 N
Maximum Von Mises stress: 60.79 Mpa
Maximum strain: 0.07 mm
Minimum safety factor: 1.81
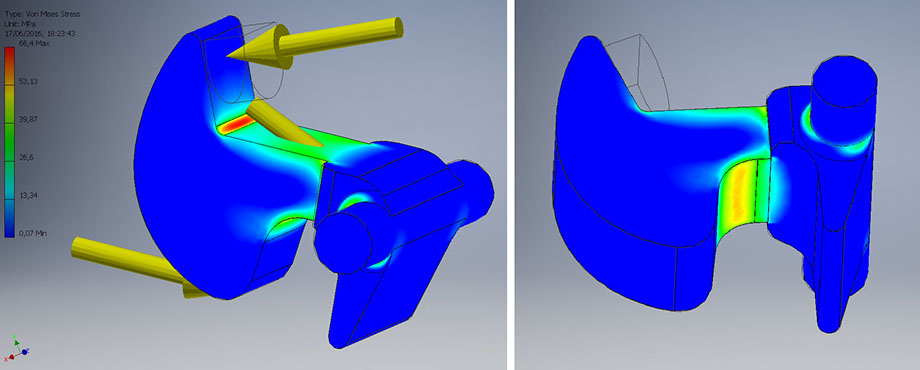
Closing: maximum load carried out by the spring
Contact force: 63.06 N
Elastic force: 66.87 N
Maximum Von Mises stress: 66.4 Mpa
Maximum strain: 0.05 mm
Minimum safety factor: 1.66
In order to develop the analysis above, dynamic simulations have been done on the mechanism, which gave back force values used in the finite element simulations. The trend of this forces is shown in the graphs below.
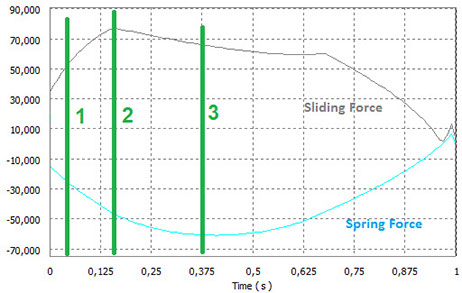
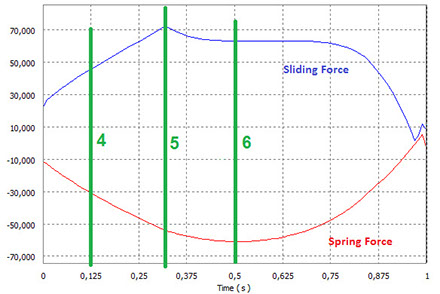
Most stressed case are, both in opening and closing pahses, those related to the maximum load carried out by the spring and by the pin.
In the opening phase, the highest concentration of stress is located mostly around the bearing cylinders, always remaning below critical stress.
In the closing phase, instead, the most stressed areas are the bottom of the cam and the fillet surface on the the top of the cam, always remeaining inside the limits of the minimum safety factor allowed.
Laboratorio Progettuale CAD - Academic year 2015-2016

